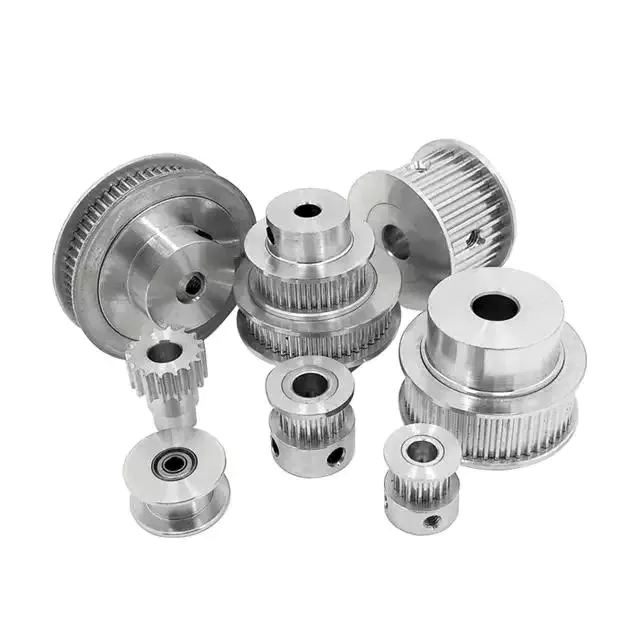
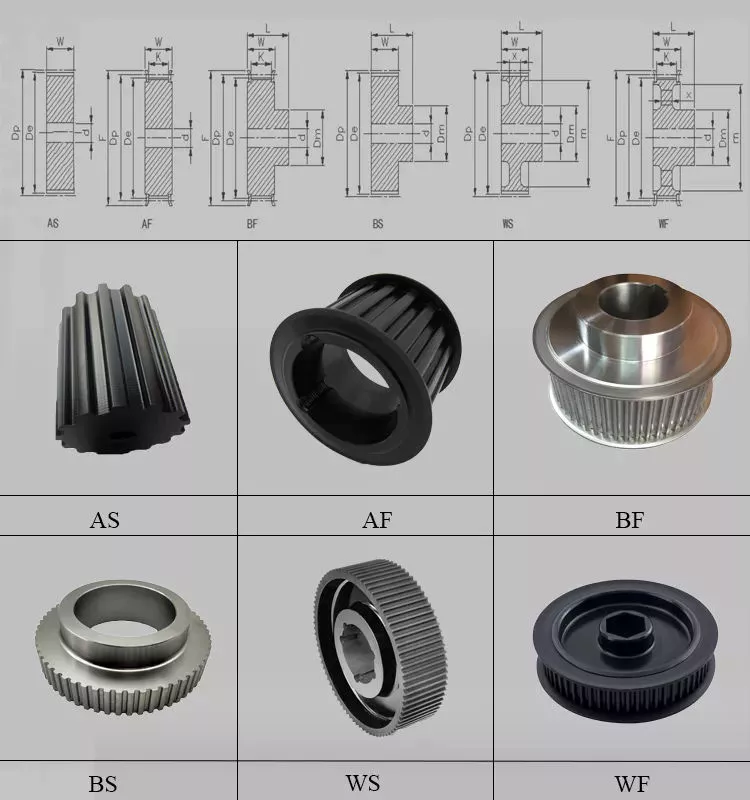
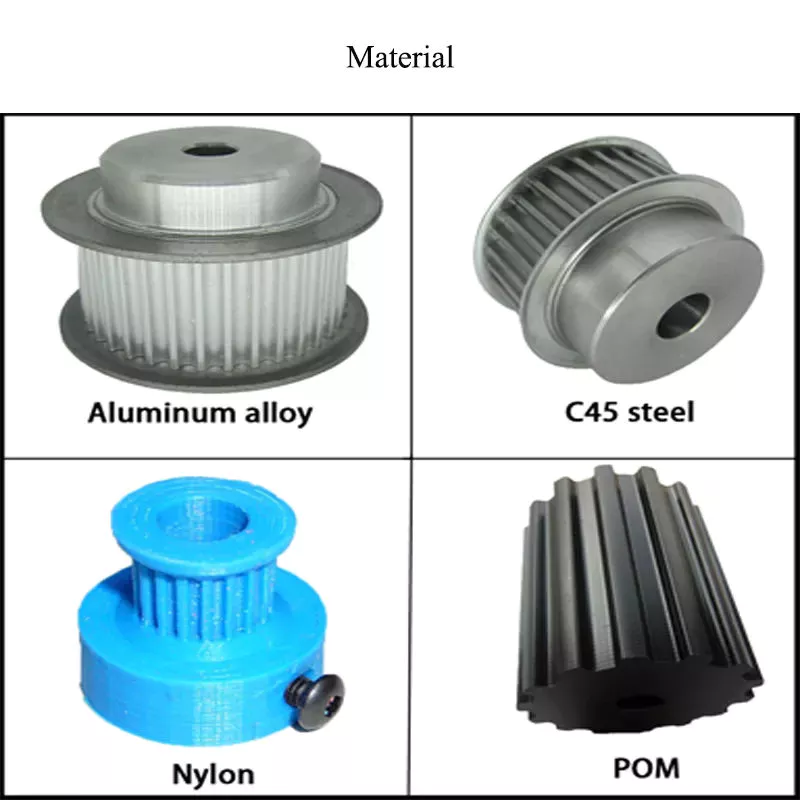
Product Description
IHF Custom Steel C45 Aluminum 20 Teeth Bore Synchronous Wheel 2GT Belt Timing Pulleys
Main Features:
1. OEM/ODM tooth number from 14 to 72 timing pulley
2. Material can be designed by customer requirement
3. High torque series S2M S3M S5M S8M P2M P3M P5M P8M
4. Normal torque series MXL XL L H
5. High precision drive series 2GT 3GT 5GT 8YU
6. Light load drive series T5 T10
7. Heave load drive series AT5 AT10
8. Clamping Timing Pulleys S3M S5M S8M
Product Parameters
| Product | Timing Belt Pulley & idler pulley |
| Teeth type | Normal Torque Drive Type:MXL,XL,L,H,XH,XXH High Torque Drive Type:S2M,S3M,S5M,S8M,HTD2M,HTD3M,HTD5M,HTD8M,P2M,P3M,P5M,P8M High Precision Position Drive Type:2GT,3GT,5GT,8YU Light Load Drive Type:T5,T10,T20 Heavy Load Drive Type:AT5,AT10,AT20 |
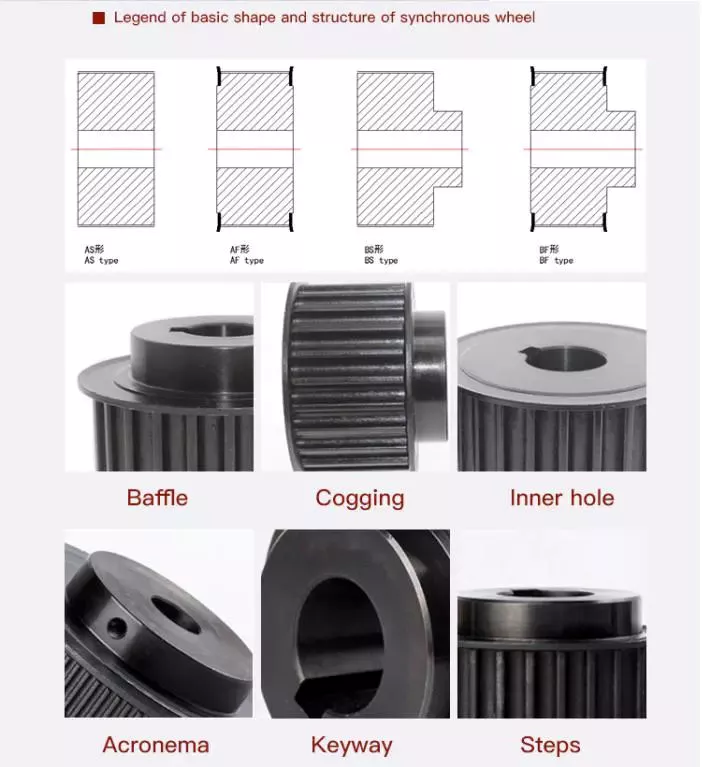
| Basic shape | Type A,Type B,Type D,Type E,Type F,Type K |
| surface treatment | Natural color anodizing,Black anodizing,Hard anodizing,Ni-plating,Blackening |
| Material | 6061(aluminum),S45C(45# steel),SUS304(Stainless steel) |
| Bore | Pilot bore, Taper bore and Customized bore. |
| testing equipment | projecting apparatus,salt spray test,durometer,and coating thickness tester,2D projector |
| producing equipment | CNC machine,automatic lathe machine,stamping machine,CNC milling machine,rolling machine,lasering,tag grinding machine etc. |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching,Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping |
| Application industry | Robot industry,Medical industry,Making machine industry,Automation industry,3C industry equipment,Packaging industry,UAV industry,New energy industry. |
| Advantages | 1.High temperature resistance,Self lubrication,Wear resistance,Flame retardant properties 2.Good quality products 3.Competitive prices 4.Fast delivery 5.Best after-sale service 6.Brand: HeFa or OEM/ ODM 7.Good service:satisfactory service before and after sale. 8.Direct manufacturers |
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
| Packaging | Polyethylene bag or oil paper for each item; Pile on carton or as customer’s demand |
| Delivery of Samples | By DHL, Fedex, UPS, TNT, EMS |
| Lead time | 10-15 working days as usual, 30days in busy season, it will based on the detailed order quantity. |
FAQ
| Main markets | North America, South America,Eastern Europe,Weat Europe,North Europe.South Europe,Asia |
| How to order | *You send us drawing or sample |
| *We carry through project assessment | |
| *We give you our design for your confirmation | |
| *We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design | |
| *You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us 30% deposit | |
| *We start producing | |
| *When the goods is done,you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers | |
| *Trade is done,thank you!! |
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Certification: | CE |
| Standard: | DIN, ASTM, GB, JIS |
| Customized: | Customized |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Application: | Machinery Parts |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
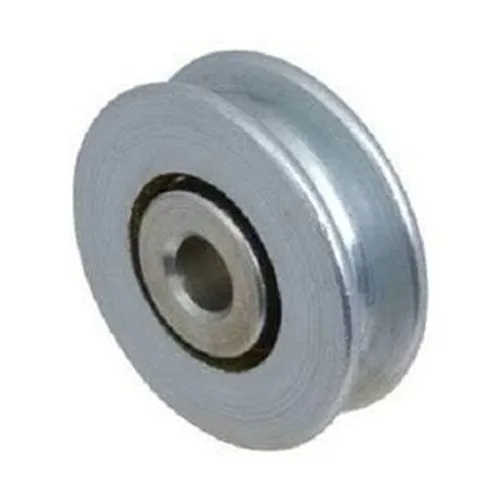

How are wheel pulleys employed in automotive engines and accessories?
Wheel pulleys play a crucial role in automotive engines and accessories, contributing to various functions and systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Serpentine Belt System:
Wheel pulleys are commonly employed in automotive engines as part of the serpentine belt system. This system consists of a single, continuous belt that drives multiple accessories and systems in the engine, such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, air conditioning compressor, and more. The wheel pulleys, also known as idler pulleys or tensioner pulleys, are strategically positioned along the belt path to guide and tension the belt, ensuring proper engagement and power transfer to the accessories.
2. Power Transmission:
In automotive engines, wheel pulleys are integral to power transmission. The crankshaft pulley, often the largest wheel pulley in the system, transfers the rotational motion from the engine’s crankshaft to the serpentine belt. The belt then distributes this power to the various accessories, allowing them to operate and perform their respective functions. Wheel pulleys enable efficient power transmission, maintaining the overall performance and functionality of the engine and its accessories.
3. Belt Tension and Alignment:
Wheel pulleys in automotive engines are designed to maintain proper belt tension and alignment. Tensioner pulleys are equipped with mechanisms that apply tension to the serpentine belt, ensuring it remains tight and properly engaged with the pulleys. Idler pulleys guide the belt along its path and help maintain its alignment, preventing slippage or disengagement. Proper tension and alignment provided by wheel pulleys are crucial for the reliable operation of the serpentine belt system.
4. Overrunning Alternator Pulley:
An overrunning alternator pulley (OAP) is a specialized type of wheel pulley used in automotive alternator systems. The OAP allows the alternator to freewheel or decouple from the engine during certain conditions, reducing drag and improving fuel efficiency. It incorporates a one-way clutch mechanism that allows the alternator to rotate freely in one direction while locking in the other direction when the engine is generating power. The OAP wheel pulley contributes to smoother operation, reduced vibrations, and improved overall efficiency of the alternator system.
5. Customization and Performance:
Automotive wheel pulleys can be customized and optimized for specific applications to enhance performance. They can be designed with specific groove profiles, dimensions, or surface coatings to maximize belt engagement, reduce noise, or improve durability. Additionally, lightweight materials such as aluminum or composite alloys are often used to reduce rotational mass and improve engine efficiency.
6. Maintenance and Replacement:
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of wheel pulleys are essential in automotive engines and accessories. Regular inspection helps identify any wear, misalignment, or damage to the pulleys or belts, ensuring optimal performance and preventing potential failures. When necessary, damaged or worn wheel pulleys should be replaced to maintain the reliability and functionality of the engine and its accessories.
Overall, wheel pulleys play a vital role in automotive engines and accessories, contributing to power transmission, belt tension, alignment, and overall system performance. Their inclusion in serpentine belt systems and specialized applications like overrunning alternator pulleys ensures the efficient and reliable operation of automotive engines and accessories.
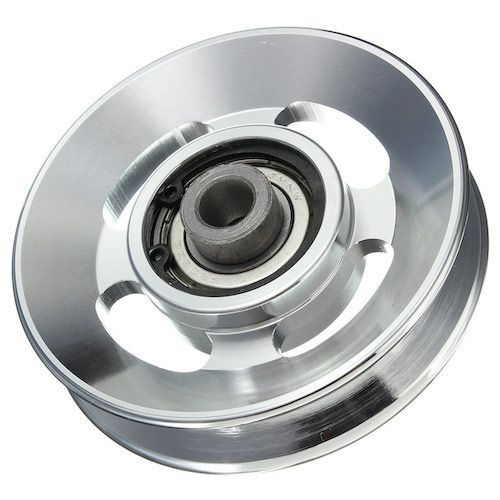

Can wheel pulleys withstand variations in environmental conditions?
Wheel pulleys are designed to withstand variations in environmental conditions to a certain extent, depending on the materials used and the specific design considerations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Temperature:
Wheel pulleys can be engineered to tolerate a wide range of temperatures. Metals like steel and aluminum have good heat resistance and can operate effectively in high-temperature environments. However, extreme temperature fluctuations or prolonged exposure to very high or low temperatures may affect the performance and integrity of certain materials, such as plastics or rubber components. In such cases, special heat-resistant or cold-resistant materials may be used for wheel pulley components.
2. Humidity and Moisture:
Some wheel pulley materials, such as steel or stainless steel, have natural resistance to moisture and humidity. However, materials like cast iron or certain types of plastics may be susceptible to corrosion or degradation when exposed to high levels of moisture or humidity. In such situations, protective coatings or sealants can be applied to enhance the pulley’s resistance to moisture and prevent rust or deterioration.
3. Chemical Exposure:
Wheel pulleys may encounter various chemicals depending on the application and industry. Certain materials, such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant plastics, exhibit good chemical resistance and can withstand exposure to common chemicals. However, aggressive or corrosive chemicals may require specialized materials or coatings to ensure the pulley’s longevity and performance.
4. Dust and Particles:
In environments where dust, dirt, or other particles are present, wheel pulleys can be designed with features to prevent the accumulation of debris. Sealed bearings or protective covers can be incorporated to minimize the ingress of contaminants, ensuring smooth operation and reducing the risk of damage or premature wear.
5. Outdoor Exposure:
Wheel pulleys used in outdoor applications may be exposed to sunlight, UV radiation, and weather elements. UV-resistant materials or coatings can be employed to mitigate the effects of prolonged sun exposure, preventing material degradation and maintaining the pulley’s performance.
6. Vibration and Shock:
Environmental conditions that involve vibrations or shock loads can impact the performance of wheel pulleys. However, the design and construction of pulleys can incorporate features such as reinforced structures, shock-absorbing materials, or dampening mechanisms to withstand these conditions and maintain reliable operation.
While wheel pulleys can generally tolerate variations in environmental conditions, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the application and select materials, coatings, and designs that can withstand the anticipated environmental challenges. Regular maintenance, inspections, and appropriate protective measures can also help extend the pulley’s lifespan and ensure optimal performance under varying conditions.

What are the primary components and design features of a wheel pulley?
A wheel pulley consists of several primary components and design features that enable its functionality in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Circular Disc:
The main component of a wheel pulley is a circular disc. This disc is typically made of a durable material such as metal or plastic. The circular shape provides a stable structure for the pulley and allows for rotational motion.
2. Groove:
One of the key design features of a wheel pulley is the groove or grooves along the circumference of the disc. The groove is designed to accommodate a belt or rope, allowing it to engage with the pulley. The shape and depth of the groove may vary depending on the type of belt or rope being used.
3. Belt or Rope Engagement:
The groove in the wheel pulley provides a secure grip on the belt or rope. This ensures efficient power transmission and prevents slippage during operation. The engagement between the pulley and the belt or rope is crucial for transferring motion and power.
4. Diameter:
The diameter of the wheel pulley determines the speed and torque characteristics of the mechanical system. Larger pulley diameters generally result in higher belt speeds and lower torque, while smaller pulley diameters yield lower belt speeds and higher torque. The diameter can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed and torque requirements.
5. Bearings:
Wheel pulleys often include bearings to facilitate smooth rotation. Bearings reduce friction between the pulley and its mounting shaft, enabling efficient motion transfer and minimizing wear on the pulley and the shaft.
6. Mounting Shaft:
A wheel pulley is typically mounted on a shaft, which allows it to rotate. The mounting shaft may be a separate component or an integral part of the pulley design. It provides the axis of rotation for the pulley and is connected to the driving or driven component of the mechanical system.
7. Material:
Wheel pulleys are commonly made of durable materials such as steel, aluminum, or reinforced plastics. These materials offer strength and resistance to wear, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the pulley.
8. Pulley Flanges:
Some wheel pulleys feature flanges on the outer edges of the disc. These flanges help guide and keep the belt or rope aligned within the groove, preventing it from slipping off the pulley. Flanges also provide additional support and stability to the pulley assembly.
9. Tensioning Mechanism:
In certain applications, wheel pulleys may include a tensioning mechanism. This mechanism allows for the adjustment of belt tension, ensuring proper engagement and optimal power transmission. Tensioning mechanisms can be in the form of adjustable mounts, springs, or tensioning pulleys.
10. Lubrication Points:
Wheel pulleys may have lubrication points to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction. Lubrication helps minimize wear and heat generation, extending the lifespan of the pulley and improving overall efficiency.
Overall, the primary components and design features of a wheel pulley include the circular disc, groove, belt or rope engagement, diameter, bearings, mounting shaft, material, pulley flanges, tensioning mechanism, and lubrication points. These features work together to enable efficient power transmission and rotational motion in mechanical systems.


editor by CX
2023-09-20